Who uses ArchiMate?
In the post below about the ArchiMate language the question 'who uses this language?' comes up. The short answer here is IT architects. The long answer is this post.

- Jacco Meijer
- |
- Mar 18, 2025
Visualizing IT Architecture in three languages, UML, C4 and ArchiMate
What are the differences and what are these languages most used for?
IT architects
This list of IT architect roles is long. This post started with the Chief, Enterprise and Solutions roles in mind but the list is longer.
Archimate perspective
From an ArchiMate perspective, the roles could be simple. A motivation architect, a strategy architect, a business architect, an application architect and a technology architect. The motivation or strategy architect overseeing the full architecture.
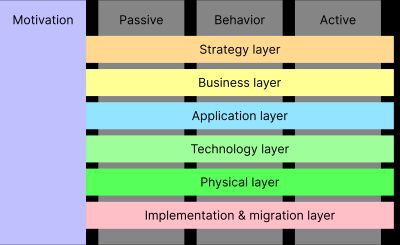
TOGAF perspective
The Open Group maintains a Framework for Enterprise Architecture known as TOGAF. The core of this framework is the TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM).
The TOGAF ADM can be mapped to the Archimate layers as shown below. The colors in the diagram match the Archimate layers above.
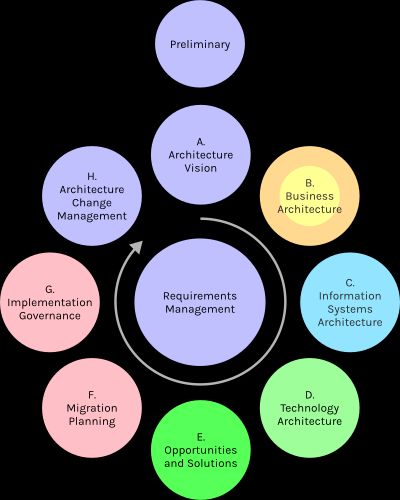
The model
In real life, IT architect roles do not follow the ArchiMate abstraction nor do the roles follow the TOGAF ADM. Many roles exist and depending on the context the expected activities vary.
This post uses the example roles from the TOGAF Architecture Roles and Skills Guide (10th edition). The guide uses the three TOGAF viewpoints for managing an enterprise architecture landscape to describe architect roles:
- A complete enterprise and its overall structure
- Specific segments (relevant elements) of the enterprise that have coherence and can be governed and evolved effectively
- Specific solutions that utilize the components within the segments to remove, change or introduce new solutions and their associated sub-systems, systems and services
The model below relates these viewpoints to the the four TOGAF defined architect roles: chief, enterprise, segment and solutions architect.
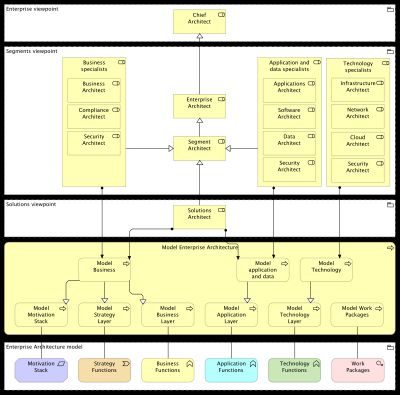
Specialists
Besides the four TOGAF defined architect roles, the segments viewpoint shows three groups of specialists. Business specialists on the left, application, data and technology specialists on the right. A similar division is found in the TOGAF architecture Roles and Skills Guide.
The two groups on the right mimic the ArchiMate layers on the bottom. Likewise the group on the left could be divided if needed.
TOGAF defined roles
The TOGAF Architecture Roles and Skills Guide contains detailed descriptions of these roles.
All architects focus on delivering services and solutions. Below how the role varies in the level of abstraction and specificity. As a general rule all architects work closely together.
Chief architect
Chief architects communicate concepts and ideas to all executives and are responsible for gaining their commitment. They lead all architects on the highest level and provide strategic alignment.
Enterprise architect
Enterprise architects work with senior stakeholders, they define architectural principles and oversee governance.
Segment architect
Larger enterprises have segment architects that handle segments of the enterprise architecture.
They are responsible for the capabilities of a segment.
Solution architect
Solution architects collaborate with business and specialist stakeholders. They make sure solutions meet requirements and ensure desired business outcomes. Part of that responsibility is that they oversee architectural and solution building blocks.
Security architect
The model defines a security architect for all three specialist groups. This is because security is a broad area. The CISSP Common Body of Knowledge (CBK) divides the profession into eight domains.
- Security and risk management
- Asset security
- Security architecture and engineering
- Communication and network security
- Identity and access management
- Security assessment and testing
- Security operations
- Software development security
Actual security architecture is covered by domain 3. But all domains can be mapped to specific ArchiMate layers. More on this in the post below.

- Jacco Meijer
- |
- May 1, 2025
CISSP certification and Enterprise Architecture
How do the CISSP certification domains relate to Enterprise Architecture and the ArchiMate layers?
Specialists
A specific architect for a specific task. This makes sense, but this also results in many different architect roles.
Brief specialist role overview
| Role | Modeling | Aligns model with |
|---|---|---|
| Business architect | Business strategy and process | Technology strategy and process |
| Compliance architect | Compliance objectives, measures and risks | Business requirements and IT processes |
| Application architect | Behavior and integration of software applications | Requirements on usability, scalability, performance and maintainability |
| Software architect | Structure and behavior of software applications | User requirements |
| Data architect | Data and data flows | Security objectives and governance |
| Infrastructure architect | Physical and virtual technology infrastructure | Requirements on availability, recovery and performance |
| Network architect | Physical and virtual network systems | Requirements on security, scalability and efficiency |
| Cloud architect | Cloud computing strategies and architectures | Requirements on security, scalability and efficiency |