Software development security
Software security is a vital part of information security, covering everything from development to deployment. It is complex to secure because it involves multilayer architecture, developer behavior and the challenges of AI. Cloud services can simplify by shifting security responsibilities to providers but this increases the complexity of compliancy and governance.
– CISSP Common Body of Knowledge
"Discussions of information security must include the security of the software powering those information systems"
Software development
The long definition of software development:
the process of designing, creating, testing and maintaining software applications or systems. It involves writing code, designing software architecture, debugging and deploying programs to meet specific needs or solve particular problems. This process typically follows methodologies like Agile or Waterfall and includes tasks like writing user stories, coding, testing and documentation.
And the short version:
the full lifecycle of building software from an idea to a finished and functional product.
The phrase 'full lifecycle' from the short description brings the topic to that was is known as the Software Development LifeCycle (SDLC).
Software development lifecycle
A search on software development lifecycle in the Dutch NEN register brings up two standards:
| Standard | Title and description |
|---|---|
| ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288 | Systems and software engineering - System life cycle processes |
| NPR 5333 | Output‑based measurement, performance management and contracting for agile software development and maintenance |
ISO 15288 is not specific for software but a common framework of process descriptions for describing the lifecycle of systems. The SDLC process descriptions can be combined with security considerations as defined by e.g. NIST SP 800-160.
The Dutch NPR 5333 is a new standard (released november 2025). It is intended to help both clients (customers) and suppliers (developers) in defining, measuring and managing agile software projects in a objective, transparent and outcome oriented way.
The new NPR 5333 standard is listed here because one of the development methods in this post is Agile Scrum.
Development methods
The SDLC covers the full process from an idea to a finished functional product and development methods define the steps in this process. Methods differ by prioritizing different values like speed, quality, flexibility and documentation.
Waterfall
One of the oldest methods is called Waterfall. Although considered outdated and inflexible for modern software development, Waterfall is still used for many smaller projects where little collaboration is involved.
The Waterfall method's inflexibility significantly impacts security because it limits the ability to iteratively assess and update security requirements throughout the SDLC.
Agile Scrum
By the early 2000s, the software industry increasingly recognized that the traditional Waterfall method was too rigid for the fast changing demands of modern development. In response, the Agile Alliance in 2001 published the Agile Manifesto from which various Agile frameworks emerged. Today, the Scrum variant is one of the most widely adopted frameworks for software development.

- Jacco Meijer
- |
- Feb 11, 2022
Agile Scrum
The Agile Scrum framework is flexible enough to be used in many different ways. Here's one way of working.
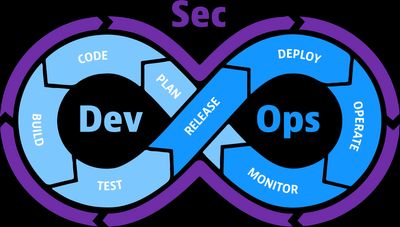
DevSecOps
Inspired by Agile practices around 2007, DevOps found its way into the world. Its adoption is often described as a cultural shift, aiming to break down the traditional silos between software development and IT operations. DevOps creates a more integrated and efficient software delivery process.
A key advantage of the DevOps culture is the acceleration of software release cycles. The increased speed however also introduced new risks by expanding the attack surface. Largely due to the fact that many security teams remained siloed and were only brought into the process late in the SDLC.
Another consequence of faster releases was that traditional compliance processes were seen as obstacles, often delaying deployments due to their slow and manual nature.
In response to these challenges, the industry began shifting toward a new cultural model known as DevSecOps where security and compliance practices are integrated in all phases of the SDLC.
DevSecOps promotes shared responsibility for security across development, operations and security teams which ensures that speed does not compromise safety or compliance.
More on the security controls for every step of this approach can be read in a post on software development security controls.
Other methods
Agile Scrum is not the only evolution of the traditional Waterfall model. While Scrum has gained widespread popularity for its iterative approach and emphasis on collaboration and flexibility, other methods have also emerged to address the limitations of the linear Waterfall process.
For example, the Spiral model introduces risk analysis and iterative development cycles, making it more adaptable to changing requirements and uncertainties.
| Concept | Waterfall | Agile Scrum | DevSecOps | Spiral |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process | Linear | Iterative | Continuous | Iterative |
| Risk | Afterwards | Managed by sprints | Continuous | Central |
| Security | Afterwards | Not inherent | Integrated | Planned |
| Flexibility | Low | High | High | Moderate |
| Project | Predictive | Evolving | Evolving | High-risk |
OWASP
A comprehensive post on software development security should not overlook OWASP, the Open Worldwide Application Security Project. OWASP is a globally recognized organization that provides a wealth of security related resources, tools and best practices for developers and security professionals alike.

- Jacco Meijer
- |
- Jan 9, 2025
OWASP and CISSP
OWASP recommendations from the independent information security certification CISSP.
SDLC Maturity
Assessing and improving the maturity of the SDLC is critical to building efficient and secure software systems. Several established maturity models help organizations evaluate their current practices and guide continuous improvement:
- Capability Maturity Model (CMM) and its successor, the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI), are foundational frameworks that focus on improving software development processes across the organization through structured levels of maturity.
- The Software Assurance Maturity Model (SAMM) developed by OWASP, specifically targets the integration of security practices into the SDLC, promoting a systematic approach to building secure software.
- The Building Security In Maturity Model (BSIMM) helps organizations benchmark their existing software security initiatives and offers practical guidance for enhancing security across the development lifecycle.
Security controls & Risk analysis
The two post below continue from here by defining DevSecOps security controls and how to analyze software development risks.

- Jacco Meijer
- |
- Oct 18, 2025
Security controls for software development
Exploring how security controls protect and improve every stage of the DevSecOps workflow.

- Jacco Meijer
- |
- Oct 19, 2025
Risk analysis for software development
By systematically identifying and assessing potential risks, teams can reduce uncertainty and prevent costly issues.
Conclusion
Software development security is a multifaceted discipline that spans the entire Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC). From initial design to deployment and beyond. As development practices evolve from Waterfall to Agile Scrum and DevSecOps, so must security approaches. Traditional methods often treated security as an afterthought, but modern methods like DevSecOps integrate security and compliance throughout the entire SDLC. This promotes a culture of shared responsibility.
The goal of software development is not just to build functional software, but to ensure it is secure, resilient and compliant in a rapidly changing technological and regulatory landscape.
As the industry continues to prioritize speed and innovation, aligning development methods with robust security practices becomes not only a technical necessity but a strategic imperative.